Introduction
In this lab we will segment and classify aerial imagery by land use in order to calculate the amount of impervious surface area per parcel of land. Some municipalities will charge home/land owners extra fees based on the amount of impervious surface area on their land because too high an amount of it can cause flooding issues.
Methods
Segment the Imagery
We first started by downloading the dataset from the ArcGIS tutorial website. The lab begins by extracting the spectral bands in order for us to better distinguish some of the urban features, like concrete, from natural features, such as vegetation. The extracted bands are 4, 1, and 3 which respectively emphasize vegetation, man-made objects, and water. Figure 1 shows the image after band extraction.
 |
| Figure 1: Extract Bands function used |
We utilize the classification wizard is used throughout much of this lab to help us classify different parts of the image. However, we leave the image segmentation alone because the next step is to create our own segmented image. The segmented image will look like Figure 2.
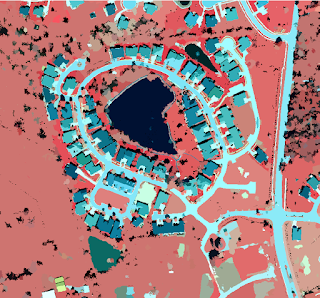 |
| Figure 2: Spectral Band Extraction on the Segmented Image |
Classify the Imagery
After the segmented image has been created, we can begin to classify the image. We classified this image into the two main classes of pervious and
impervious, within these two classes we have smaller classes to
represent types of land cover. We create training samples to classify
the imagery. Training samples are polygons that represent specific areas
of different land cover type. We created seven groups of training
samples for our image. These groups were grey roofs, roads, driveways,
bare earth, grass, water and shadows. Figure 3 below shows our
classified image with the colors we have chosen for each training
class.
 |
| Figure 3: Classified Image |
 |
| Figure 4: Training Samples |
After classifying the image we then reclassify any errors in
classification. If the data shows misclassifications we can go back and
change them manually. I did not change any of the classifications in my
data set. The resulting image is shown in Figure 5, this image shows
only pervious and impervious surfaces.
 |
| Figure 5: Pervious and Impervious Surfaces |
Now we can begin to calculate surface area. We start by creating
accuracy points, we made 100 points. These are shown in Figure 6 and 7.
 |
| Figure 6: Accuracy Points |
 |
| Figure 7: Accuracy Points Attribute Table |
In the attribute table we must manually go in and change ground truth to
20 or 40 depending on the location of the point with 20 being pervious
and 40 being impervious. Next, we computed a confusion matrix and
tabulated the area. A confusion matrix will determine the accuracy of
the classified and GrndTruth attributes. The confusion matrix results
are shown in Figure 8 below.
 |
| Figure 8: Confusion Matrix |
Tabulating the area will show the pervious and impervious area within each parcel, this is shown in Figure 9 below.
 |
| Figure 9: Tabulated Area |
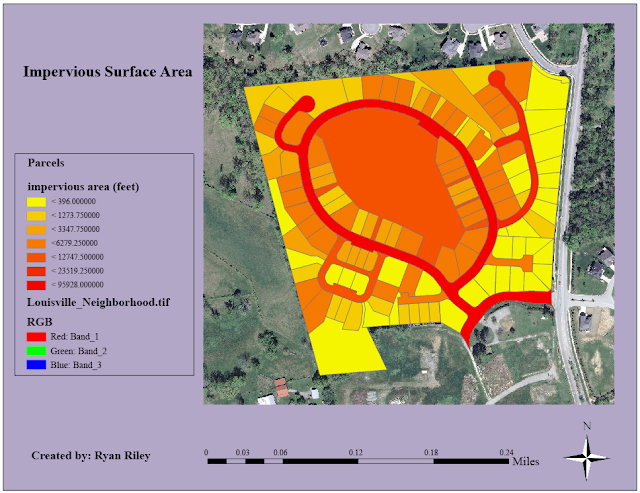
Now that we have calculated the impervious surface are we need to
symbolize the parcels. We chose a yellow to red gradient to symbolize
surface area. The symbolized parcels are pictured in Figure 10 below.
 |
| Figure 10: Symbolized Parcels |
Conclusion
 |
| Figure 11: Map of Impervious Area |
In the map we are able to analyze the amount of impervious surface area
per each individual land parcel. Local governments and civil
institutions can utilize this data to determine storm water bills. We
can determine how much impervious surface are each parcel has by
comparing the color on the map with the corresponding color in the
legend. As we can see the road contains the most impervious area of all
the parcels which is what we had expected.






Comments
Post a Comment